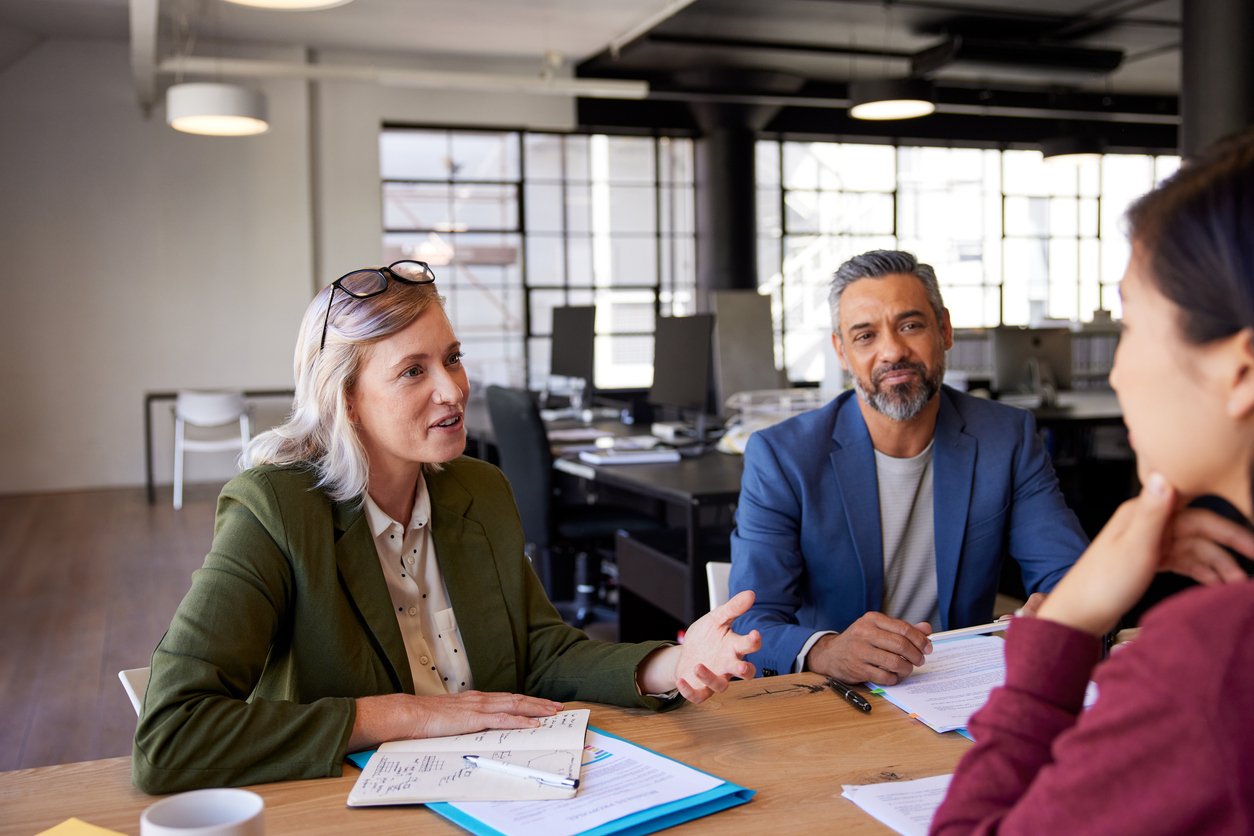
Who Is a Nonexempt Salaried Employee?
Under California labor law, employees are classified as either exempt or nonexempt based on:
- Job duties
- Salary level
- Level of independent decision-making
Exempt vs. Nonexempt Employees
- Exempt employees are not entitled to overtime pay and must meet strict salary and job duty requirements.
- Nonexempt employees are protected by wage and hour laws, meaning they must receive overtime pay when applicable.
- Being salaried does NOT automatically mean exempt—many salaried employees are still eligible for overtime.
How Is Overtime Calculated for Nonexempt Salaried Employees?
In California, overtime pay is required when a nonexempt salaried employee works:
- More than 8 hours in a single workday(1.5x regular rate)
- More than 40 hours in a workweek (1.5x regular rate)
- More than 12 hours in a single workday (2x regular rate)
- 7 consecutive workdays in a row, with double time after 8 hours on the 7th day
Calculating the Regular Hourly Rate
To determine overtime pay, the employee’s salary must be converted into an hourly wage:
- Divide the annual salary by 52 weeks (to get the weekly salary)
- Divide the weekly salary by the number of hours worked per week (usually 40 hours)
- Multiply by 1.5 or 2 for overtime hours worked
Example:
- A salaried nonexempt employee earns $1,000 per week
- Regular hourly rate = $1,000 ÷ 40 hours = $25/hour
- Overtime rate = $25 × 1.5 = $37.50/hour for overtime hours
- Double-time rate = $25 × 2 = $50/hour for hours over 12 in a day
Employer Responsibilities and Violations
Employers must track hours worked by nonexempt salaried employees and pay overtime correctly.
Common Overtime Violations
- Misclassifying employees as exempt to avoid paying overtime
- Forcing employees to work “off the clock” without overtime pay
- Failing to provide meal and rest breaks required under California law
What to Do If You Are Denied Overtime Pay
If your employer has failed to pay you overtime wages, you can:
- Keep detailed records of hours worked and pay received
- Report the violation to the California Labor Commissioner
- Consult an employment attorney to file a wage claim or lawsuit
Nonexempt salaried employees in California are entitled to overtime pay when they work beyond 8 hours per day or 40 hours per week. If you believe your employer has misclassified your job or denied overtime wages, call Law Advocate Group today at (310) 651-3065 or fill out the form below so that we may get in touch with you as soon as possible.